Green design for Greener buildings : Mastering the strategies
By Mz Chaker & EAGC, 2024
With Green Design, let’s explore how to balance beauty, efficiency & sustainability in Modern Architecture !

In today’s world, the need to adopt Green Design for buildings is more urgent than ever. As the climate crisis worsens, our approach to creating buildings becomes a principal factor in environmental degradation. Traditional building methods continue to leave damaging carbon footprints, harming ecosystems and depleting natural resources. Yet, amidst this challenge lies a potential solution: Sustainable Architecture. By integrating green practices into our designs, we can create a healthier, more sustainable future for both the planet and the communities.
But how do we get there, and what are the strategies to make a real difference? This article dives deep into the main principles of Green Building Design. What core strategies should architects adopt to reduce energy use and enhance sustainability? How can sustainable materials and systems reshape the future of construction? As we explore these questions, you will gain valuable insights into building for a greener tomorrow. Join us on this exploration!
1. The Basics of Green Design In Architecture
Core Concepts and Definitions
In Sustainable Architecture, Green Design is an approach focused on creating buildings that reduce environmental impact throughout their lifecycle. That includes careful planning, designing, constructing, and maintaining buildings. In doing so, it aims to promote energy efficiency, water conservation, and waste reduction.
Moreover, this approach focuses on minimizing resource consumption, enhancing occupant well-being, and ensuring a balanced relationship between the building and the environment. However, it’s not just about adding eco-friendly features. Instead, it involves integrating these elements into the entire building life cycle, from design and construction to operation and maintenance.
Key Sustainable Architecture Objectives Behind Green Design
Sustainable architecture is the backbone of Designing Green Buildings. It focuses on creating eco-friendly buildings that benefit both communities and the environment. Below are the key principles that guide this approach:
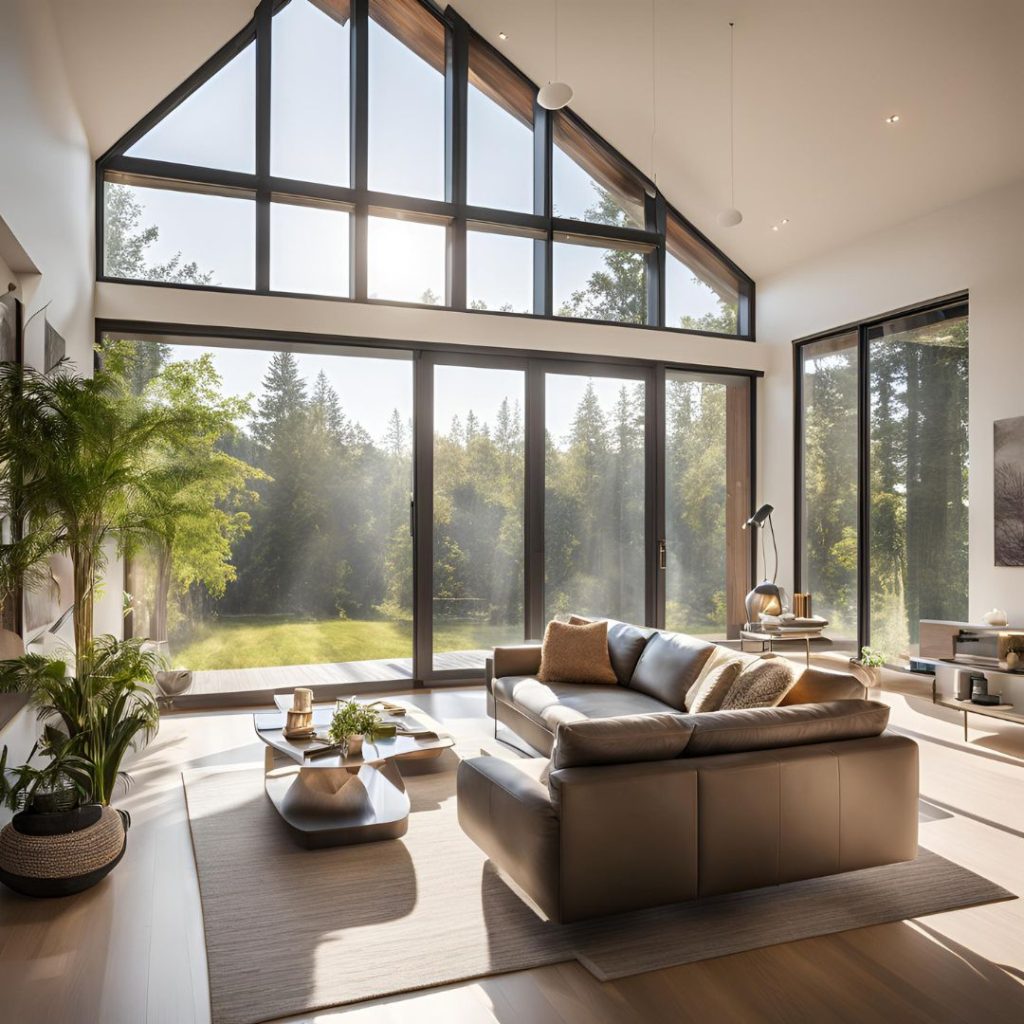

- Maximizing Natural Light: Using natural light to reduce reliance on artificial lighting.

- Optimizing Energy Use (Energy efficiency): Combining insulation, renewable energy sources, high-performance windows, etc.

- Promoting Resource Efficiency: Minimizing waste during construction and operation.

- Enhancing Indoor Air Quality: Incorporating proper ventilation systems, non-toxic materials, and air filtration systems.

- Renewable and Low-Impact Materials Incorporation using recyclable or low-impact materials

- Water Conservation: Implementing water-saving fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and greywater recycling.
These principles, when combined, create buildings that meet current needs while preserving resources for future generations. In addition , sustainable architecture encompasses several other key principles that further contribute to long-term environmental and societal benefits:

- Building Longevity and Flexibility: Designing for durability and adaptability, with flexible designs that can be adapted to meet future needs, reducing frequent renovations or replacements.
- Site Selection and Land Use: prioritizing previously developed or urban sites to minimize sprawl and avoid disrupting natural habitats.

- Biodiversity and Ecosystem Support: Integrating natural elements like green roofs, living walls, and landscaping with native species. These features provide habitat for wildlife and promote ecological balance in urban environments.
Evolution of Green Building design : A Historical Perspective
The concept of Green Design has evolved significantly in Architecture field over the past decades. Initially, it began as a niche practice with a small, dedicated following. Early green buildings focused mainly on low-level energy efficiency and reducing water use. However, as awareness of environmental issues grew, the movement gained momentum. Gradually, green building practices became more sophisticated, incorporating advanced technologies and innovative materials.
Today, the Green design of buildings use energy-smart systems, solar panels, and recycled materials to enhance sustainability. This shift reflects a broader understanding of the urgent need for sustainable living. Moreover, it represents a direct response to the escalating climate crisis. As a result, Green Building Design has become a powerful, mainstream movement. It continues to evolve, adapting to new challenges and opportunities to protect our planet for future generations.
2. Design Strategies for Greener buildings
Passive Design Techniques: Letting Nature Work for You
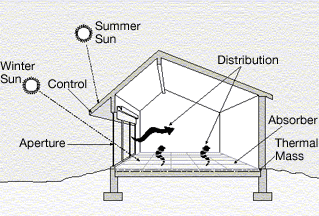
Passive design strategy makes the most of natural resources. Using sunlight, wind, and shade helps maintain a comfortable temperature year-round. For example, designers often rely on building locations to capture sunlight and heat in winter while offering shade in summer. This thoughtful approach reduces the need for heating and cooling systems.
Moreover, passive design uses simple features like wide eaves, large windows, and strategic landscaping. Wide eaves can block harsh summer sun, while large windows let in light during colder months. In addition, skillful landscaping with trees and plants provides shade and helps cool the air. Ultimately, these methods cut energy costs while making spaces more pleasant. By letting nature do the work, passive design creates homes and buildings that are both eco-friendly and cost-effective.
Innovative Energy Solutions: Solar, Wind, and Beyond


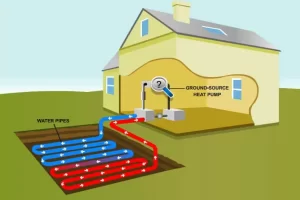
Renewable energy solutions are crucial in Green Building Design. At the core, solar panels capture sunlight and turn it into electricity. Likewise, wind turbines harness the power of the wind to generate clean energy. In addition to these options, geothermal systems tap into the Earth’s natural heat to provide heating and cooling.
By using these technologies, buildings reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, which are harmful to the planet. Moreover, they help lower greenhouse gas emissions, which cause climate change. Beyond reducing emissions, these solutions also offer long-term savings on energy bills. Ultimately, integrating solar, wind, and other innovative energy sources represents a crucial step toward a more sustainable future.
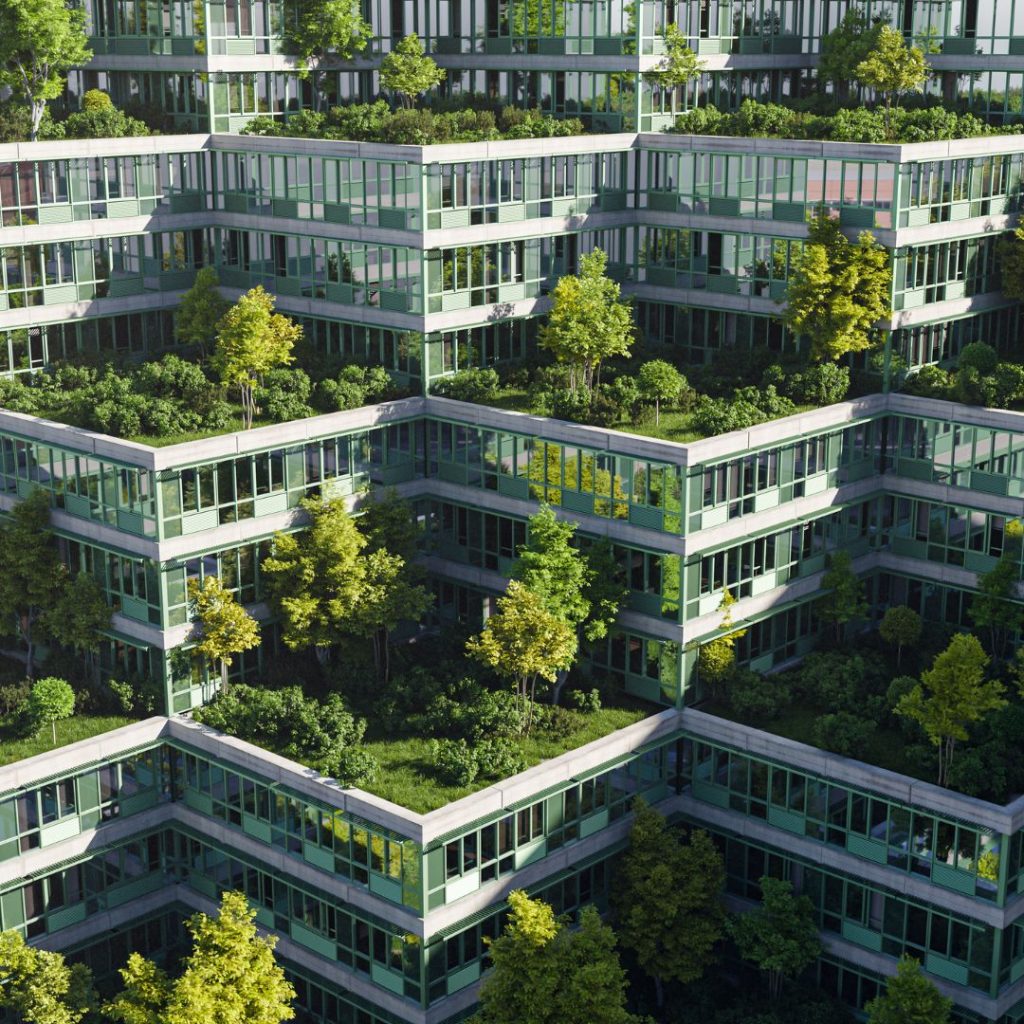

Green Roofs and Living Walls: Integrating Nature into Design
Green roofs and living walls bring nature back into cities. They add layers of greenery to urban buildings, making them more sustainable. By insulating rooftops and walls, these features help regulate indoor temperatures and lower energy consumption. Moreover, green roofs reduce urban heat by absorbing sunlight that would otherwise reflect off hard surfaces.
Additionally, these living elements improve air quality by filtering pollutants and producing oxygen. They also support local wildlife, providing habitats for birds, insects, and other species in dense urban areas. Beyond these environmental benefits, green roofs and walls enhance the visual appeal of buildings, creating vibrant and lush landscapes. Incorporating these features into urban design fosters ecological balance, boosts biodiversity, and makes cities more livable and beautiful.
Efficient HVAC Systems: Keeping Cool and Green
Efficient HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems are vital in green building design. They reduce energy use while keeping spaces comfortable year-round. These systems use advanced technologies to heat, chill, and ventilate buildings with less energy. High-efficiency units, like heat pumps and energy recovery ventilators, maximize performance and cut power consumption.
Furthermore, smart thermostats and automated controls are crucial in managing HVAC systems. They adjust temperatures based on real-time data, reducing waste and lowering costs. With these innovative tools, buildings can respond to changing conditions, maintaining comfort efficiently. Efficient HVAC systems are a core part of sustainable design. They ensure that green buildings remain both eco-friendly and cost-effective.
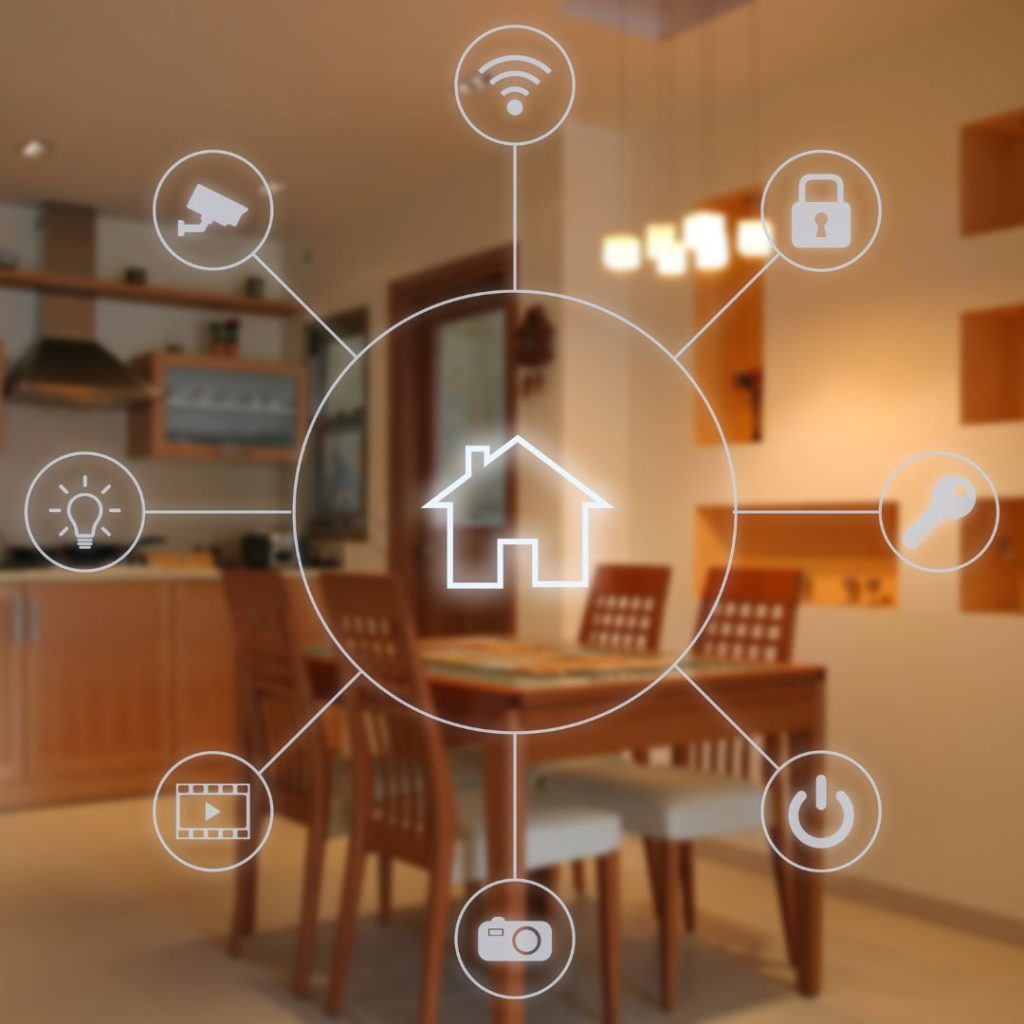

Smart Building Technologies
Smart technologies are transforming the landscape of Green Building Design. Automated lighting, climate control, and energy management help buildings operate more efficiently. Building-wide sensors can monitor temperature, humidity, and occupancy levels, providing real-time data for optimal adjustments. Moreover, data analytics enable precise tracking of energy consumption, revealing patterns that help reduce waste and lower costs.
In addition, Smart technologies make buildings more adaptable and responsive to occupants’ needs. Indeed, automated systems can adjust lighting or HVAC settings based on occupancy, improving comfort while saving energy. These technologies enhance not just the efficiency of buildings but also their ability to minimize environmental impact, making smart technologies essential for modern green design.
3. Overcoming Challenges in Green Building Design
Navigating Budget Constraints: Cost-Effective Green Solutions
In Green Building Design, Budget constraints often present challenges. Yet, many affordable strategies can still achieve sustainability. For example, using local materials not only supports the local economy but also helps to reduce transportation costs and emissions. Further, opting for modular construction methods can lower expenses by reducing waste and speeding up the building process.
Similarly, integrating energy-saving technologies, like LED lighting and efficient HVAC systems, can minimize long-term operational costs. While initial investments might seem high, these solutions pay off through lower utility bills and maintenance costs. Creative planning, such as building orientation optimization and passive design techniques, helps reduce energy demands. By making smart choices and focusing on practical solutions, green buildings can remain both accessible and affordable. That is how sustainability and budget-consciousness can come together.
Addressing Regulatory Hurdles: Compliance and Innovation
Navigating regulations in Green Building Design can be challenging, yet it is vital for ensuring safe and sustainable practices. Understanding local building codes, such as energy performance standards and environmental guidelines, is crucial for compliance. These regulations often dictate specific aspects like energy efficiency, water use, and material selection.
However, green designers must also innovate to meet both regulatory demands and sustainability goals. That often involves creative problem-solving and the use of cutting-edge technologies. For instance, implementing new materials or building techniques can help satisfy strict codes while enhancing a building’s green credentials. Furthermore, finding this balance between compliance and creativity drives growth and innovation in the field.
Adapting Traditional Designs: Integrating Green Principles Seamlessly
Adapting traditional building designs to meet green standards requires a blend of innovation and respect for heritage. Retrofitting existing structures with sustainable materials, such as recycled wood or low-impact concrete, helps maintain the cultural significance of historic buildings. At the same time, incorporating energy-efficient systems like solar panels, modern insulation, and intelligent climate controls reduces energy consumption.
This approach not only preserves the architectural identity of communities but also enhances the environmental performance of their buildings. By creatively integrating green principles, architects can honor the past while preparing for a sustainable future. Moreover, these adaptations inspire other communities to see the potential of their traditions, making green design a shared and accessible goal for everyone
Adapting Green Building Design for Different Climates and Geographies
Green building design must fit the local climate and geography to be effective. Cooling strategies like natural ventilation, shading, and reflective roofing are essential to reduce heat gain in warm areas. Meanwhile, using insulation and passive solar heating helps retain warmth and reduce energy costs in colder climates.
Designers should also consider local weather patterns, such as heavy rainfall or strong winds, and adapt building materials and structures accordingly. So, green buildings can achieve higher performance and sustainability by respecting natural conditions and using local resources. Ultimately, adapting a Green Design to each location ensures its efficiency and sustainability, no matter where it stands.
4. Implementing Green Building Practices
Navigating Green Certifications
Green certifications like LEED and BREEAM provide explicit standards for sustainable building practices. Earning these certifications shows a firm commitment to sustainability and often boosts a building’s market value. Moreover, these certifications offer guidelines on energy efficiency, water use, and materials, helping projects align with global standards.
However, the process can be complex, as each certification has specific criteria and requirements. Understanding these standards is essential to ensure your project meets all necessary benchmarks. Additionally, working with experts familiar with these certifications can simplify the journey. Ultimately, navigating these certifications can elevate your project, demonstrating its value and sustainability to clients and communities.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Investing in Green Design
Investing in Green Building Design provides substantial long-term benefits. While the initial costs may be higher, the savings accumulate over time. For example, green buildings significantly reduce energy bills and lower maintenance expenses. Moreover, these buildings often have a longer lifecycle, thanks to durable and sustainable materials.
Conducting a cost-benefit analysis is essential to understand the financial value of green investments. It helps identify both short-term expenses and long-term savings, offering a clearer picture of the overall impact. Additionally, this analysis can support decision-making by showing stakeholders the financial gains and environmental benefits. Thus, a well-planned investment in green design can bring lasting returns, proving its worth in many ways.
5. Case Studies: Successful green design Projects
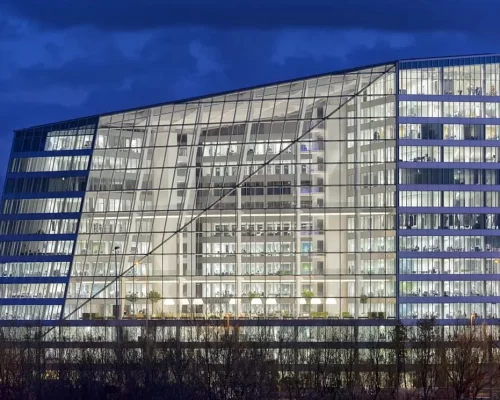

The Edge in Amsterdam by @ Ronald Tilleman on WIRED

One Central Park, Sydney by @Giantflightlessbirds

The Brock Environmental Center in Virginia @ By Jwallace72 on Wikimedia
Many successful green building projects worldwide are providing valuable lessons and inspiration. These case studies showcase innovative designs, intelligent strategies, and advanced technologies that achieve remarkable results. For example :
- The One Central Park building in Sydney, Australia, is a striking skyscraper that uses solar panels, green walls, and smart energy systems to reduce its environmental footprint. Its vertical gardens help regulate temperature while providing natural beauty.
- On the other hand, the Edge in Amsterdam, Netherlands, is one of the smartest and most sustainable office buildings worldwide. It features innovative technologies, such as a smart energy management system powered by over 65,000 solar panels that generate more energy than the building consumes. The Edge also uses rainwater harvesting systems for non-potable water, advanced insulation, and floor-to-ceiling windows that maximize natural light.
- Community centers, like the Brock Environmental Center in Virginia Beach, also shine as examples. This building uses passive design, sustainable landscaping, and renewable materials to create a harmonious balance between the built environment and nature.
These examples prove that sustainability can coexist with aesthetics and functionality. They demonstrate that thoughtful planning and creative solutions can lead to beautiful, efficient, and eco-friendly buildings. By showcasing that it is possible, these projects inspire others to adopt green practices, highlighting the potential for a more sustainable future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering green building design is more than a trend; it is a movement toward a sustainable future. By understanding the core principles and applying intelligent strategies, creating eco-friendly and efficient buildings becomes possible. You can play a role by making informed choices, from selecting sustainable materials to supporting green initiatives in your community.
Starting your green building project might seem daunting, but small steps can lead to ample changes. Begin with energy-efficient upgrades, or consider eco-friendly materials for your next renovation. Many resources and tools are available to guide you through the process, from online courses to certification programs like LEED and BREEAM.
Ultimately, every effort counts. By promoting eco-friendly practices, we all help build a brighter, greener future. Let us commit today to designing a world that thrives for tomorrow’s generations.